







Obesity is a medical word that describes a level of being overweight that can or is seriously affecting health and wellbeing. Obesity has become a serious health problem in Australia with 65% of the population being overweight and up to 25%, obese. The Body Mass Index (BMI) measurement is used to compare weight to height and is a good and reliable indicator of the degree to which an individual is overweight.
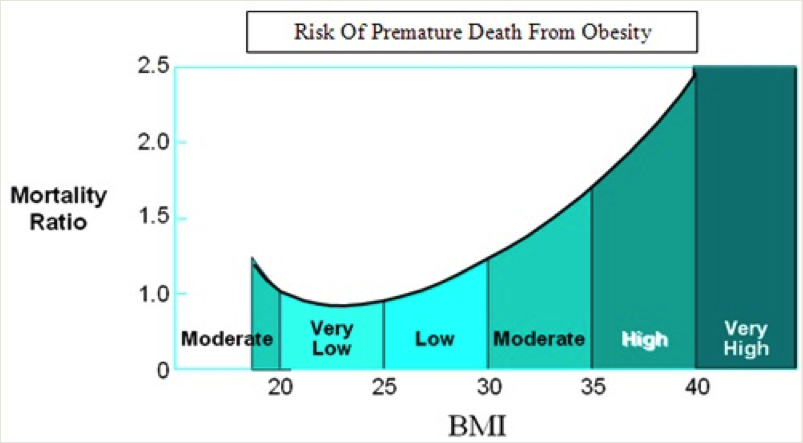
A BMI of 18-25 is considered to be a healthy weight range. A BMI higher than this indicates that the individual is overweight and health may be at risk. The greater the degree of overweight, the greater the health risk posed. Once the BMI is over 30, risk to health is significant. Individuals are considered obese if their BMI is 30 or greater. BMI Calculator (use a BMI calculator here)
Today up to one in five people are considered obese. Obesity may cause or make worse many diseases. The risk of developing Type II diabetes for instance is 400% greater in obese people than the non obese.
What are the Obesity Weight Loss Options?Obesity is now the single most important cause of “preventable premature death.” For individuals whose BMI ranges between 37 and 40, the risk of an early death is doubled compared to non-obese individuals.
Of course, obesity has significant impact on quality of life and just doing everyday things like using transport, buying clothes, playing with children or just getting around. It also affects our general well being and self esteem.
Weight gain occurs when the amount of energy consumed (as food) is greater than the amount of energy expended (activity). Excess energy is stored in the body as fat. Eating high calorie foods or eating too much food and not exercising enough certainly sets one up for the increased possibility of becoming overweight.
This often leads people to feel that the reason for their weight problem is simply lack of discipline or laziness. After all, all you have to do is eat less and exercise more… Simple isn’t it! That of course is the most difficult advice to follow.
As anyone who has had a weight problem will tell you, it is incredibly frustrating when you try and try but just can’t seem to keep the weight off! It is easy to feel like a failure. It’s easy to think “… but I should be able to do this!!”
Obesity and overweight is a difficult and complex problem.
Yes, discipline, good food choices and a healthy lifestyle are just as important as are social circumstances, social support and psychological factors.
However, it is clear that there are biological and genetic factors that predispose people to being overweight and obese. That is why obesity often runs in families. These genetic factors primarily control appetite and food intake but to some extent, energy expenditure too. Basically, people with a genetic tendency toward obesity are able to eat large amounts of food before feeling full and often describe more hunger than non-overweight people. Furthermore, when they lose weight, various hormonal changes occur. This hormonal change is naturally designed by the body to increase appetite and put the weight back on.
Our modern society is such that food, and often high energy food, is readily and cheaply available. Furthermore, at every turn modern technology means we have to do less and less physically. If you have the genes for obesity, this sort of environment makes it impossible to avoid weight gain. With these changes in our environment over the last decade, obesity has increased rapidly – the so called “obesity epidemic”.
The following have been identified as important contributing factors in becoming overweight or obese: